Research Subjects
Hydrological Processes
Flux measurement --> more
Remote sensing Application -->
Glacier and snow melting -->
Runoff analysis -->
Water Resources Analysis
Snow water resources --> more
Nutrient and fertilization -->
Economic evaluation -->
Health risk assessment -->
Ecology and Water
Habitat estimation --> more
Genetic diversity -->
Climate Change
Flood damage cost projection --> more
Landslide projection -->
Hydrological Processes
Flux measurement
We are measuring latent and sensible heat fluxes to know energy balance
on the surface. This measurement can be used for understanding of thermal
environment and energy cycle. The results are applied to urban planning
and reduction of water loss by evapotranspiration.

Measurement system of fluxes on a tower in Thailand
(Komori et al., Journal of Agricultural Meteorology, 60(5), pp.529-532, 2005)
Remote sensing Application
Remote sensing provides wide information for water cycle. Albedo on glacier
and evapotranspiration on vegetation areas are estimated using multi-spectral
sensors.
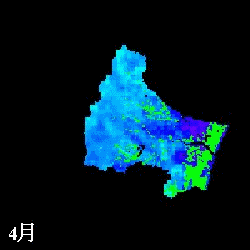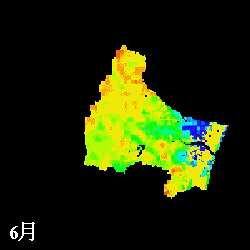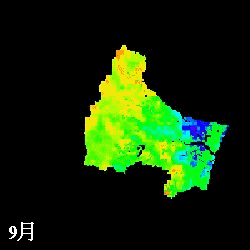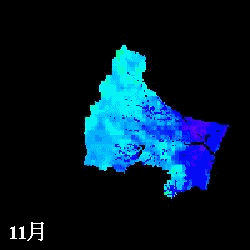
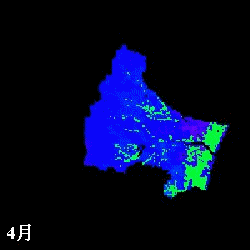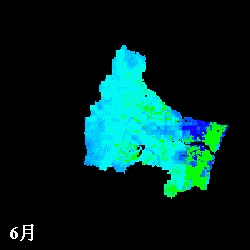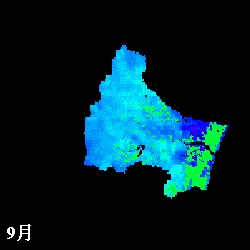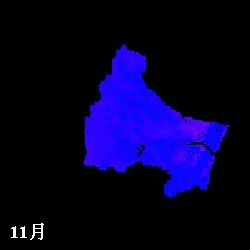
 mm/month
mm/month
Evapotranspiration from April to November estimated in the Natori River
Basin using NDVI
L: direct NDVI method, R: Single Layer model
(Watanabe et al., IAHS Red Book, 289, pp.392-400, 2004.)
Glacier and snow melting
Glacier and snow are the most sensitive for global warming. The disappearance
of glacier affects not only water resources but more global warming. We
are measuring glacier and snow and developing models estimating the change.

Snowboarding with high accurate GPS to measure snow surface elevation in
Zao Mt.
Runoff analysis
Runoff simulation can tell us about water movement in a basin and and risk
of drought and flood. We must consider distribution of precipitation,
evapotranspiration, surface and subsurface flow. Also storage of snow and
paddy field is important. Runoff model integrates all hydrological processes.
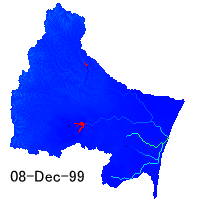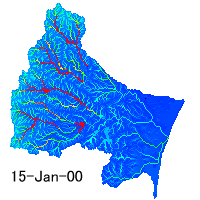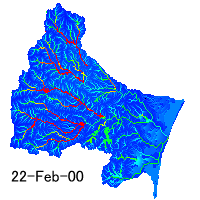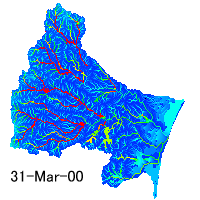

Distribution of water depth in the Natori River Basin simulated by a hydrological
model
Water Resources Analysis
Snow water resources
Snow is called a white dam in Japan. The storage water is huge and used for rice planting in spring season. How large does snow storage amount correspond to paddy field? How much will we miss out on paddy field after global warming? We seek those answers.
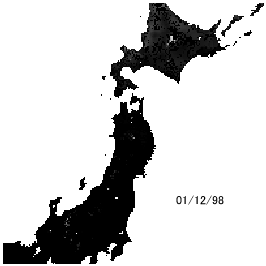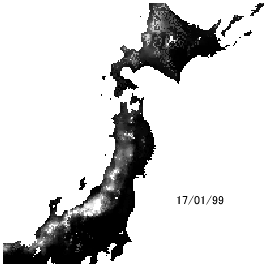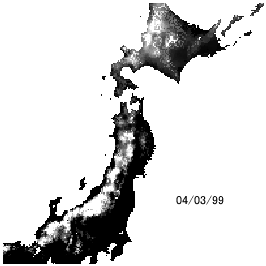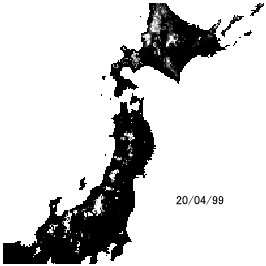

Snow depth change simulation in Japan
(Kazama et al., Hydrological Processes, 22(13), pp.2315-2324, 2008.)
Nutrient and fertilization
Flood inundation in the Mekong River produces many benefits such as fishery
production, groundwater resources and fertile grounds. The fertilizer effect
of the inundation produces sustainable crop production if farmers plant
suitable number of crops. To know this, we measure the amount of nutrient
in inundation areas.

Water sampling and analysis in Cambodia
(Amano et al., Journal of Water and Environment Technology, 10(2), pp.165-175, 2012.)
Economic evaluation
Evaluation of cost and benefit of water is helpful for comparing with other
items. Especially the future projection can contribute to ground design
and developing planning. This areal study needs economics and mathematics
for numerical modeling.
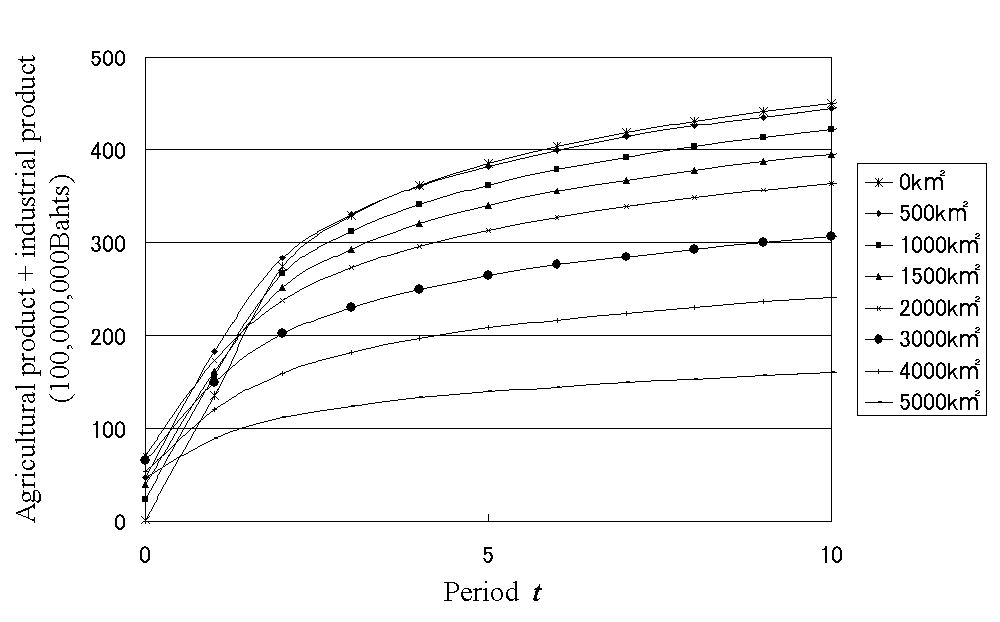
Relationship between benefit products and inundation area in time series
in the lower Mekong. Zoom in this to see mode details.
(Kazama et al., Hydrological Processes, 23(4), pp.623-632, 2009. )
Health risk assessment
Inundation water brings not only nutrient but also bacteria and virus. These are one of the most serious risks in flood. So that, it is waterborne infectious disease. Numerical simulation estimating the risk was developed depending on land use, diffusion of E.coli and flood water depth. We can understand high and low risk areas by the simulation results.
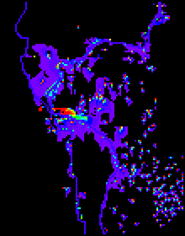
The infection risk of surface water use on middle flood magnitude in the
lower Mekong
(Kazama et al., Sustainability Science, 7(1), pp.45-54, 2012.)
Ecology and Water
Habitat estimation
Hydrological conditions are highly related with water creature habitat.
This means that hydrological model will evaluate habitat of aquatic organism.
This concept was introduced by HSI on HEP. Here HSI is Habitat Suitability
Index and HEP is Habitat Evaluation Procedure.
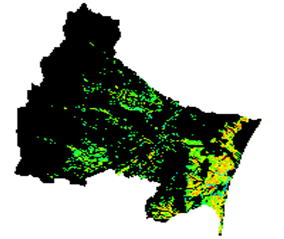
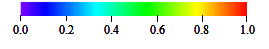
HSI distributions of Luciola lateralis (Japanese firefly, Heike Hotaru) in the Natori River Basin
(Nukazawa et al., Ecological Modelling, 222(20-22), pp.3718-3726, 2011.)
Genetic diversity
Integration of results for several species by above method can evaluate
species diversity. On the other hand, we are observing genetic information
of benthic insect in rivers. Comparing these, we will estimate genetic
diversity in a basin under much discussion.

Benthic animals collection in Wasada River
Climate Change
Flood damage cost projection
When we consider the adaptation for climate change, an option in the adaptations
should be discussed in view of the cost. A damage cost map in the future
supports decision making for the adaptation in spatial and temporal.
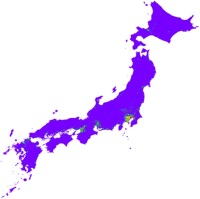
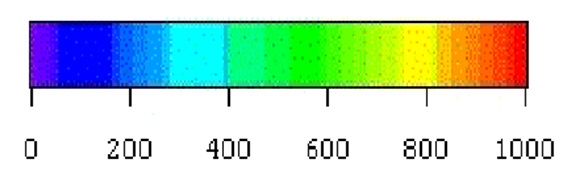 million USD
million USD
Distribution of increase of potential damage cost from rainfall with 50- to 100-year return periods
(Kazama et al., Sustainability Science, 4(1), pp.61-69, 2009.)
Landslide projection
Heavy downpour affects not only flooding but also landslide. Japan is covered
with steep mountains and landslide is the frequent water disaster. A future
projection map can discuss the countermeasure for slope failure with landuse
and population data.
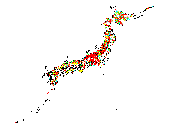
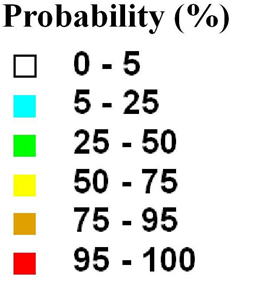
Developed landslide hazard probability maps for extreme precipitation in
30 years return period
(Kawagoe et al., Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 14, pp.1047-1061, 2010.)












 million USD
million USD
